How to Calculate the Perimeter of a Right Triangle
By the end of this lesson, you will be able to
- calculate the perimeter of a right triangle.
- find the perimeter of any right-angled triangle although its one side is missing.
The perimeter of a right triangle is the total length of its three sides. There is a set of techniques how to calculate the perimeter of a right triangle. A right-angled triangle is a special type of triangle whose one of the angles is 90°. The sides of a right-angled triangle have special names: base, perpendicular and hypotenuse. So, the perimeter of any right triangle is obtained by adding the length of base, perpendicular and hypotenuse.
This content guides you through how to find the perimeter of a right triangle by applying different formulas depending on different situations.
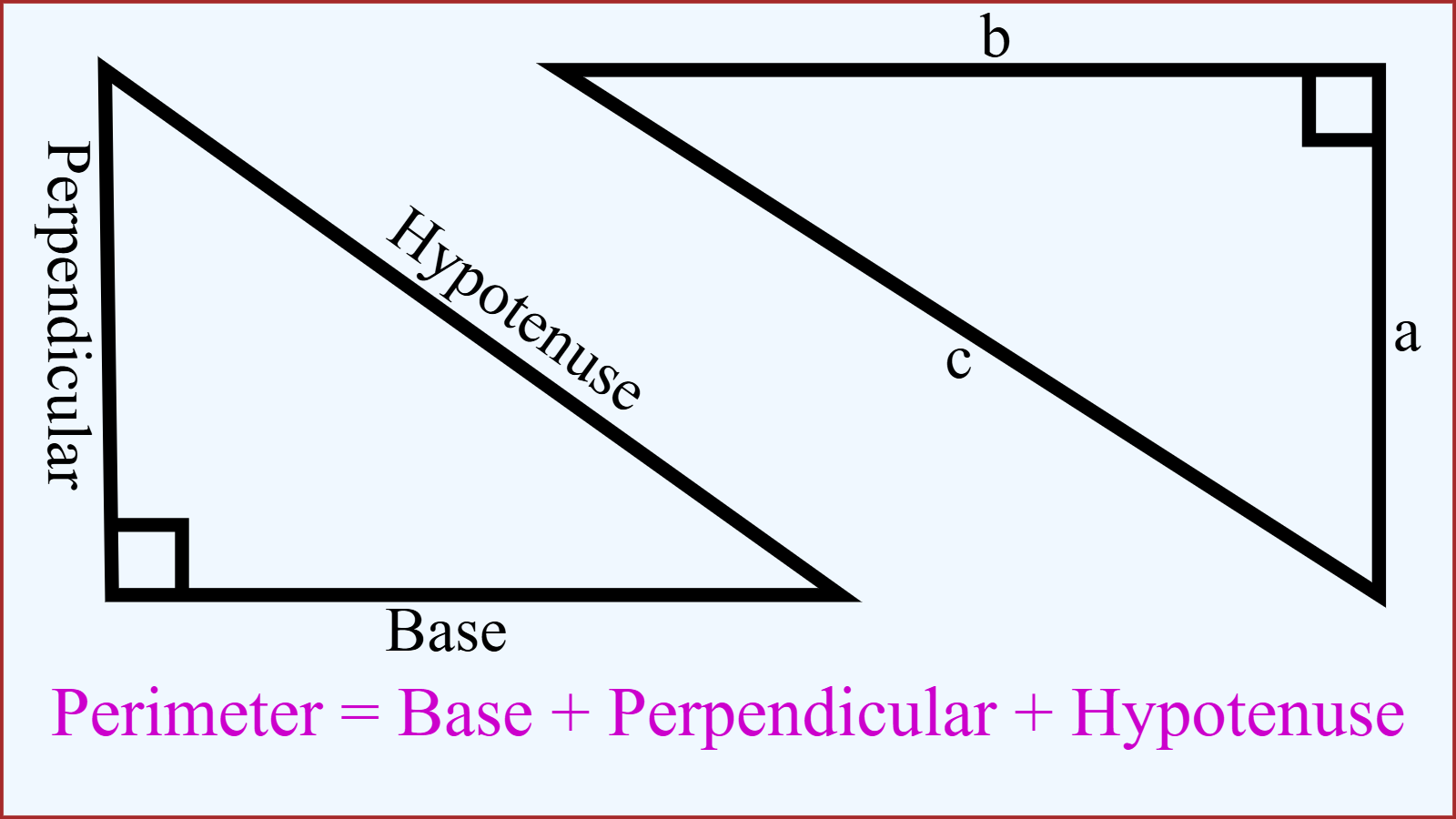
The three sides of a right triangle have special names. Let's introduce all three sides of a right triangle.
- Hypotenuse: The side opposite the right angle. It is always the longest side.
- Perpendicular: The side opposite one of the acute angles (angles less than 90°).
- Base: The side adjacent to one of the acute angles.
Calculating the Perimeter
The perimeter of any triangle is the sum of the lengths of all its sides. In the case of a right-angled triangle, three sides are base, perpendicular and hypotenuse. Hence, the perimeter is:
Perimeter = Perpendicular + Base + Hypotenuse
Perimeter = Perpendicular + Base + Hypotenuse
Example 1: The three sides of a right angled triangle are 5 cm, 12 cm and 13 cm. How to calculate the perimeter of that right triangle?
Solution: Let the base of the right triangle be 5 cm, perpendicular = 12 cm and hypotenuse = 13 cm.
∴ Perimeter = Perpendicular + Base + Hypotenuse
or, Perimeter = (12 + 5 + 13) cm
∴ Perimeter = 30 cm
There are various techniques and formulas to evaluate the perimeter of a right triangle based on given sides. Let's explore the different strategies and formulas relevant to the perimeter of a right-angled triangle.
Finding the Hypotenuse
If you know the lengths of the perpendicular and base, you can calculate the hypotenuse using the Pythagorean Theorem:
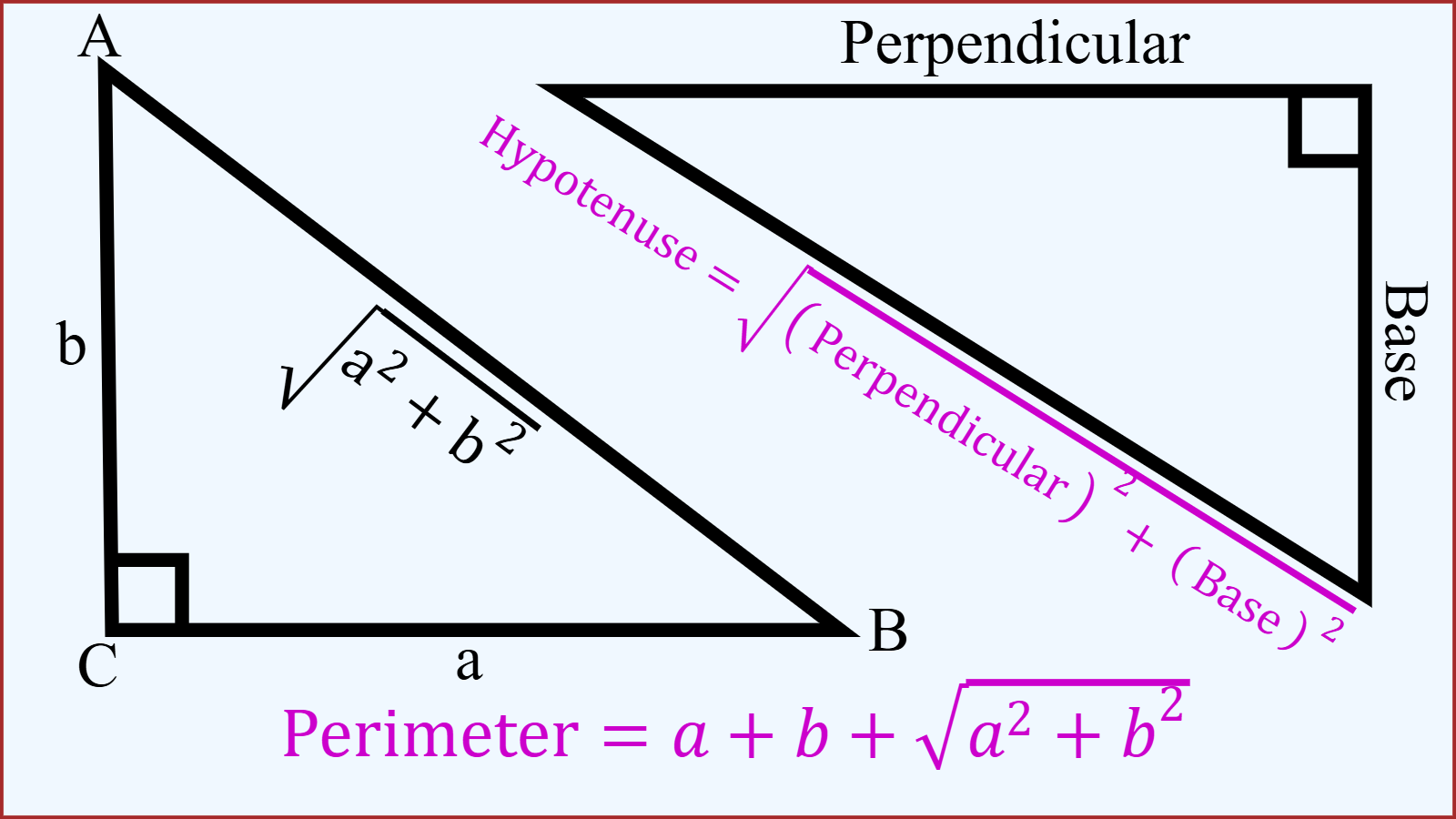
Example 2: Suppose, you have a right-angled triangle with perpendicular of 3 meter and base of 4 meter. Determine the perimeter of this right triangle.
Solution: Given that the base a = 3 meter and the perpendicular b = 4 meter. Let the hypotenuse be c meter. We know, So, the Hypotenuse is 5 meter.
Again, we have
Perimeter Based on Base and Perpendicular
If you have a right-angled triangle whose two sides: base and perpendicular are given but the hypotenuse is not provided, you can surely obtain the perimeter of this right triangle.
Let ABC be a right-angled triangle where ∠C = 90°. And the base BC = a unit and perpendicular AC = b unit are given. But the hypotenuse c is unknown.
Applying Pythagorean Theorem on the right triangle ABC, we can write
Now,
If the base is a unit and the perpendicular is b unit,
Example 3: A right-angled triangle with base 7 cm and perpendicular 24 cm. How to find the perimeter of the right triangle?
Solution: Let ABC be the right triangle with ∠C = 90°. Suppose the base BC = a = 7 cm and perpendicular AC = b = 24 cm.
According to the perimeter formula for the right triangle, we have Hence, the perimeter is 56 cm.
Perimeter Based on Hypotenuse and Perpendicular
Suppose, there is a right triangle whose Hypotenuse and Perpendicular are given but the length of Base is missing. Can you calculate the perimeter of the right triangle? Yes, you can!
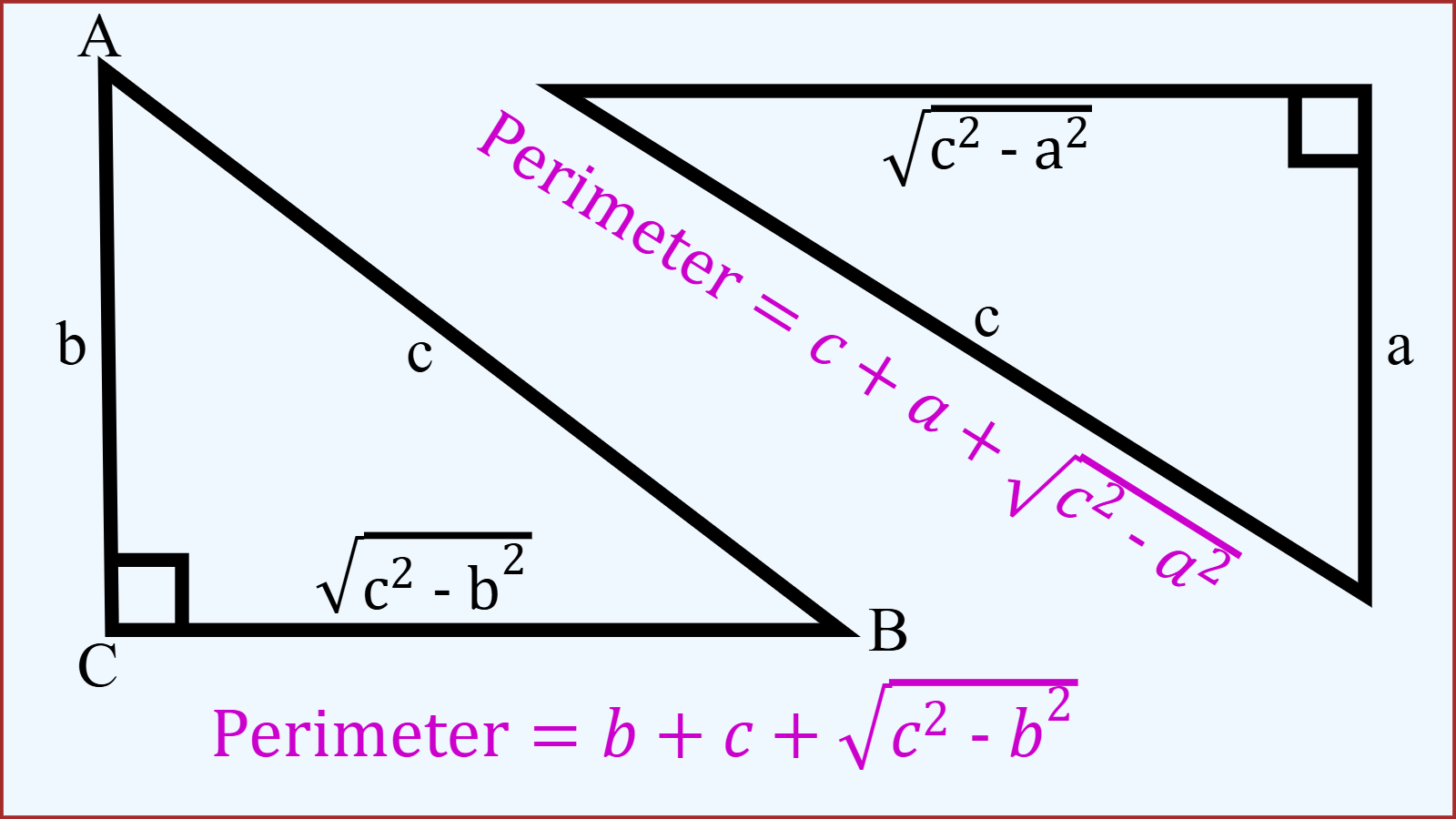
Consider right-angled triangle ABC where ∠C = 90°. Let Hypotenuse be AB = c unit and the Perpendicular AC = b unit are given. But the Base a is missing.
According to Pythagorean Theorem on the right triangle ABC, we have
Let's derive the perimeter formula,
If the perpendicular is b unit and the hypotenuse is c unit,
Example 4: A right-angled triangle with perpendicular 8 cm and hypotenuse 17 cm. How to calculate the perimeter of a right triangle?
Solution: Let ABC be the right triangle with ∠C = 90°. Suppose the perpendicular AC = b = 8 cm and hypotenuse AB = c = 17 cm.
So the perimeter formula, Therefore, the perimeter of the right triangle is 40 cm.
Perimeter Based on Hypotenuse and Base
If the Hypotenuse and the Base of a right triangle are given but the distance of Perpendicular is missing, you are able to calculate its perimeter.
Consider a right-angled triangle ABC where ∠C = 90°. Suppose, its Hypotenuse be AB = c unit and the base BC = a unit are given. But the Perpendicular b is unknown.
By applying the Pythagorean Theorem, we have
Let's try to form the perimeter formula,
If the base is b unit and the hypotenuse is c unit,
Example 5: If the base of a right-angled triangle is 12 cm and hypotenuse 37 cm. How to obtain the perimeter of this right triangle?
Solution: In our right triangle with ∠C = 90°; let the base be BC = a = 12 cm and the hypotenuse AB = c = 37 cm.
We have the perimeter formula, Therefore, the perimeter of the right triangle is 84 cm.
Key Points:
The Pythagorean Theorem plays an important role for finding the missing side of a right-angled triangle. The perimeter of any triangle, including a right-angled triangle, is the sum of its sides. I hope this content helps you!